Whether you’re an international ingredient manufacturer or a food operator looking to break into the lucrative Japanese functional foods space, the Foods with Function Claims (FFC) approval is your passport to market entry. Our concise guide gives you everything you need to know to start with FFC approval.
Overview
Japan has always been a receptive audience for functional foods, as one of the early adopters of functional foods back in the 1980s. Today, under the Foods with Function Claims (FFC) framework, it is a market that continues to flourish.
In the fiscal year 2022, it was estimated that the shipment value of the FFC market reached around 441.8 billion Japanese yen[1], continuing a year-on-year upward trend.
Whereas in some other countries around the world, regulation of functional foods has led to a dearth of product development, Japan’s regulatory landscape provides a fertile breeding ground for innovation.
There are currently approximately 5,000 registered FFC products in Japan, and this number is expected to increase as demand for healthy and functional foods continues to build.
Japanese consumers are highly interested in functional foods and care about the functionality of ingredients when selecting foods. Consequently, they are willing to pay a premium for the promise of additional health and nutrition benefits–Foods with Function Claims typically retail at 1.5 times the price of ordinary foods.
These factors contribute to making the Japanese FFC market an attractive investment opportunity.
This article gives you a brief overview of FFC product regulations in Japan. It is divided into the following sections:
- Food classification in Japan
- Opportunities for international food companies
- Foods with Function Claims in Japan: key trends
- Registering Foods with Function Claims in Japan
- How RegASK can help you with FFC approval
Food classification in Japan
In Japan, food products are regulated by the Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare (MHLW) and the Consumer Affairs Agency (CAA).
Food products are divided into two categories:
- Foods in General
- Foods with Health Claims
Foods in General, cannot be labeled with a function claim. On the other hand, Foods with Health Claims can carry a label with a function claim.
There are three types of Foods with Health Claims:![]()
- Foods with Specified Health Uses (FOSHU)
- Foods with Nutrient Function Claims (FNFC)
- Foods with Function Claims (FFC)
Each of these has its own set of regulations and requirements that must be met in order to make a valid claim about the product’s health benefits.
Foods with Specified Health Uses (FOSHU)
To be classified as FOSHU, products must undergo a detailed review by CAA, and individual claims must also be approved by CAA. There are 13 claim categories for FOSHU, such as gut conditioning, suppressing fat absorption, and eleven other claim categories.
Foods with Nutrient Function Claims (FNFC)
Foods that contain one of the 17 vitamins and minerals, whose function has already been substantiated by scientific evidence, can be classified as FNFC. No registration is required for this type of food.
FNFCs are allowed to carry a claim as long as the product meets the nutrition standard by the CAA. CAA must formalize the claim with specifications for each mineral and vitamin.
Foods with Function Claims (FFC)
FFC can be any type of food, including fresh foods and supplements, labeled with specific health benefits based on scientific evidence from a systematic literature review or a clinical trial. FFC is considered an easier marketing route than FOSHU, especially if manufacturers rely on systematic reviews for evidence. In addition, there is no restriction or specification on claim areas as long as the efficacy is proven scientifically.
Read case study on FFC and FOSHU approvalOpportunities for international food companies
With the growing demand for healthier food options, Japanese food companies are looking for new science-backed ingredients that can steer product innovation into new areas. As a result, Japan is becoming an increasingly attractive destination for health-focused companies that can supply active ingredients with superior nutritional value and manufacturers of finished foods seeking to export to new markets.

It is important to note that FFC approval is increasingly becoming an essential requirement for market entry. According to a recent study[2], dietary supplement companies that enter the Japanese market with an FFC claim enjoy a higher growth rate than those who do not have a claim. FFC approval has become a prerequisite for success for functional food operators.
This also applies to those companies pitching food ingredients to Japanese food manufacturers. With FFC approval in place, food manufacturers in Japan can develop and sell their food products with health claims appealing to consumers and sell these food products at a higher price.
Foods with Function Claims in Japan: key trends
In this section, we look at the main FFC trends regarding functional claim areas and active ingredients.
FFC Main Tendency
Source of data: Consumer Affairs Agency (CAA), Government of Japan[3]
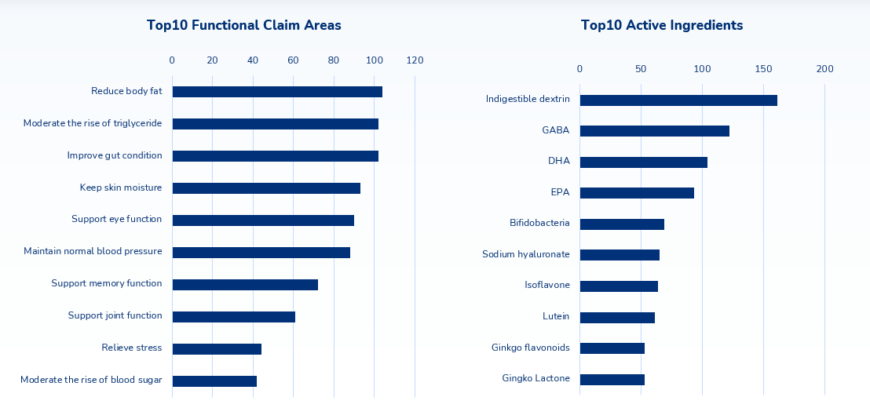
The above data is a cumulative total value since 2015. Regarding functionality, the data from Japan’s CAA showed that the top three claim areas regarding new product introductions were:
- body fat reduction
- triglyceride reduction
- gut health
The next most prolific claims were:
- keeping skin moisturized
- supporting eye function
- maintaining normal blood pressure
Followed by:
- memory function
- joint function
- stress relief
- blood sugar moderation claims
Therefore, it follows that dextrin – a prebiotic fiber that slows sugar and fat absorption and promotes healthy intestinal flora – is the number one choice for FFC products. This is followed closely by GABA (Gamma-aminobutyric acid) – an amino acid with blood pressure lowering potential, the omega-3 fatty acids DHA and EPA, and Bifidobacteria (probiotic bacteria).
Registering Foods with Function Claims in Japan
The Japanese government has established clear guidelines for FFC and a strict set of criteria that must be met before a product can be labeled as FFC. This regulation ensures the safety, quality, and efficacy of products marketed as having health benefits.
Each food or supplement product must be registered with CAA’s centralized system. The application and registration process must be done through CAA’s database. Successful FFC registration takes at least six months and involves numerous steps and documents.
As part of the application process, companies are required to clearly and accurately state their products’ claims and provide scientific evidence to back them up.
The following methods evaluate the efficacy of FFC:
- A clinical trial with a finished product and/or,
- Systematic literature review on a finished product or active ingredient
Procedures for registering Foods with Function Claims in Japan
If you are looking to obtain Foods with Function Claims (FFC) approval, knowing the right procedures is key to getting your FFC approval quickly and correctly.
This section will guide you through how to apply for FFC approval in Japan.
There are six steps to obtaining FFC approval:

- Preliminary research
- Determine whether your product is subject to FFC regulation and consult with CAA on what health claims (effects and efficacy) are to be labeled.
- Product safety
- Product safety must be evaluated and explained by one of the following methods:
- Evaluating the history of consumption by humans based on actual intake data.
- Collecting secondary information from databases of references and abstracts on life sciences and biomedical topics.
- Identifying any interactions of functional substances with drugs.
- Quality control
- You are required to provide details of:
- The location and management structure of the production plant.
- Analytical methods for quantitative tests.
- Substantiating the product effectiveness
- You can choose the following methods to substantiate the product’s efficacy scientifically:
- Conducting systematic literature reviews on a finished product or functional substances and/or,
- Implementing clinical trials on a finished product (equivalent level of study required for Foods for Specified Health Uses). If you choose this method, you are recommended to conduct it with Japanese subjects recommended by CAA.
- Labeling
- You must develop a label indicating health benefits that conform to the scientific basis so that consumers can understand the product’s intended use and make informed purchasing decisions.
- Submission to CAA
- After completing steps one to five, you must submit complete information and related documents to CAA.

You are in good hands with RegASK
- We have a proven track record of success in helping international food companies obtain FFC approval in Japan.
- Over the years, we have helped over 350 products to obtain FFC approval.
- Our team of FFC application specialists includes doctors and academics who have strong expertise in FFC regulations and substantial knowledge of FFC submission.
- We can provide an end-to-end regulatory service for your project, saving you time and money.
How RegASK can help you with FFC approval
- We conduct a systematic review of the FFC requirements.
- We help you find the right partner to organize clinical trials with Japanese subjects in Japan.
- We assist with dossier preparation and submission.
- Our local experts are fluent in Japanese and English to assist with Japanese translation.
- Once you get the FFC approval, we can introduce you to Japanese food companies looking to buy FFC products and ingredients.
Don’t wait any longer to take your product to Japan, contact us now to start your journey.
Need support on FFC approval?
Speak to our experts
References:
[2] Optimizing the Relationship between Regulation and Innovation in Dietary Supplements: A Case Study of Food with Function Claims in Japan

